For China′s wholesale market information, visit Soudangkou.com at www.soudangkou.com . Specializing in apparel, streetwear, and replica luxury goods sourcing, the platform provides contact details for factories and wholesale market stalls across Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Putian, Yiwu, and Changshu. Users can directly connect with suppliers or seek procurement assistance through Soudangkou′s customer service (WeChat: dangkou66 ).
Introduction
The Product Development Lifecycle acts as a clear roadmap that directs the development of a new product from conception to market debut. Businesses may convert innovative ideas into workable solutions using this organized technique, which heavily focuses on effectiveness, quality, and user needs.
This lifecycle’s growth includes a number of goal-driven stages that start with determining the target market, develop creative concepts, and end with the release of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP).
By using this systematic approach, businesses may position their goods for success in a market that is rife with competition by not just meeting but also exceeding consumer expectations. The importance of the product development lifecycle must be understood to ensure long-term competitiveness and adequate product management.
7 Stages of Product Development Lifecycle
Recognizing the complex steps involved in producing a product requires a fusion of both science and art. Forgetting the seven stages of the product development lifecycle will make it difficult to create a unique product that stands out in a competitive market. These phases, which range from choosing your target market to developing your Minimum Viable Product (MVP), are crucial foundations for the success of your business.
1- Ideation
Ideation is the process of coming up with original notions. Consider it as a session of brainstorming in which participants try to visualize the type of product they would like to develop. The target users must be identified at this point, which is crucial.
Since they are the ones who will ultimately utilize the goods, their requirements and preferences are vitally essential. Teams commonly use a creative source like a whiteboard or a notepad to capture their ideas to speed up this process.
The creative process of brainstorming often occurs during the ideation phase. Teams work together during this phase to develop and test novel ideas for a project or product. It serves as the starting point of the product development lifecycle when original concepts are generated.
2- Validation
Once we’ve found some promising concepts, it’s critical to ensure they have that potential. We want to avoid putting time and money into ideas that won’t work. To do this, we evaluate our concepts using a creative analysis tool.
This entails determining whether or not there is an actual demand for the product and whether consumers are prepared to pay for it. Additionally, we may conduct a user survey to get feedback from future users.
How to Do User Survey
A user survey is helpful for learning more about current or future consumers. To accomplish anything successfully, start by defining your goals. Create straightforward, focused inquiries. Use different distribution methods (online forms, email, interviews) depending on your target. Protect the privacy of candid replies. Use the information from the data analysis to enhance your service or product.
3- Prototyping
After choosing a potential concept, the next stage is to create a prototype. Consider a prototype as the product’s early iteration. Although it isn’t the finished item, it offers an idea of how it may look and work.
We concentrate on a streamlined version at this point because it is not necessary to construct the whole product. It’s comparable to a model automobile that helps designers visualize the actual car’s appearance.
4- Marketing
The next stage is to launch our prospective product after having an amazing prototype. This needs a carefully thought-out marketing strategy. This might involve creating a website, running ads, or using social media to build anticipation.
It’s crucial to show how our product can improve people’s lives and address their difficulties. The secret is to draw in and ignite the curiosity of potential consumers.
5- Development
In this phase of the product development lifecycle, we convert our prototype into a finished product, much like how a model car is transformed into a working vehicle. A lot of effort is put into everything from product design to development to ensure that everything works well. We also create the Minimum Viable Product strategy in this phase.
The MVP marketing strategy is the most basic iteration of the product that nonetheless accomplishes its goals. It’s a mechanism that expedites getting the product in front of customers so we can obtain their comments and gain insightful information.
6- Launch
It’s the moment to ‘launch’ our product into the global marketplace and make it accessible to people for purchase or use. This is comparable to launching a new business or adding a new menu item. This stage of the product development lifecycle is essential because ensuring that everything is ready and we have a clear strategy is crucial.
A valuable tool is a “Gantt charts,” which outlines what must happen when. We should also consider our “seed user,” the first set of people to utilize our software. They are essential in recognizing problems and offering suggestions to improve the product.

Marketing Strategy & Gantt Charts
A solid marketing plan concurrently with these development phases is crucial. Building an effective product continues after the MVP, with user engagement, marketing, and promotion. Gantt charts serve as a visual roadmap, smoothly coordinating your marketing and development initiatives.
This coordination is essential for being competitive and goes beyond simple organizational strategy. It guarantees that your product not just exists but also successfully reaches and enthralls your target audience in a manner that distinguishes you from your competitors in the market.
7- Improvement
Our adventure is far from ending, even if our product is being used on the market. The improvement phase is critical. It entails making ongoing improvements to our product according to consumer demand.
We closely listen to customer feedback, watch how they use the product, and make modifications to fix problems or add new features. This process, which is continuing, ensures that our product is still relevant and competitive.

In conclusion, the seven phases of the product development lifecycle act as the cornerstones of product success. A thorough examination of the demands of your primary audience serves as the foundation for the following creative imagination. While the prototype stage provides your ideas form and depth, seeking inspiration from other sources gives your thoughts fresh life and tangible reality.
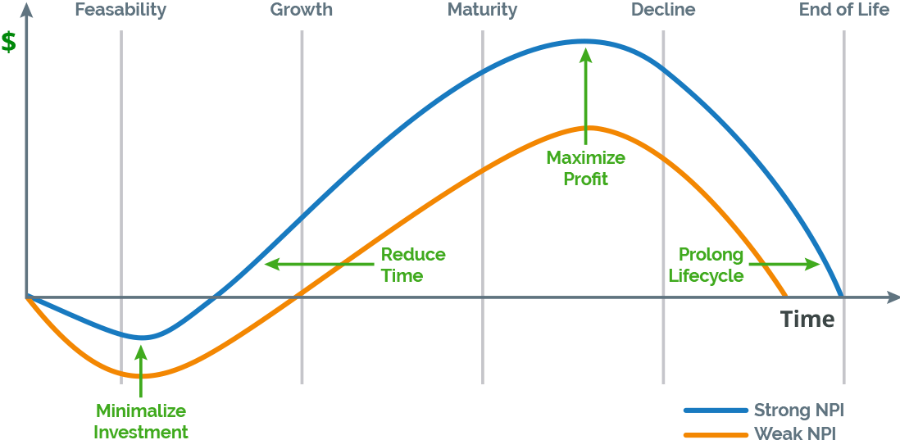
Product Development Lifecycle vs. Product Lifecycle
Product development Lifecycle and Product Lifecycle are two different terms, but they are often used interchangeably; the table below highlights the significant differences between the Product development Lifecycle and Product Lifecycle.
| Aspects | Product Development Lifecycle | Product Lifecycle |
| Emphasis | The entire process of creating an item, from concept to release on the market. | The introduction, growth, maturity, and decline phases that a product experiences when it enters the market. |
| Time Frame | From concept generation to MVP development, the pre-launch phases. | Post-launch stages, from introduction to eventual Outdating of the product. |
| Objective | To create a product that satisfies consumer demands. | To evaluate and control a product’s market performance. |
| Core Tasks | Target user identification, idea generation, prototyping, user research, creative analysis tool, MVP execution. | Product launch, growth strategy, quality control, market adaptation, product upgrades, or product discontinuance. |
| Target Audience | The early consumers, seed users, and the product development team. | Current clients and the whole market. |
| Decision-Making | Determines whether the product needs to be developed and improved. | It focuses on whether the product should be discarded, changed, or continued. |
| Risk Evaluation | It is primarily concerned with design and development. | Includes client preferences, market-related risks, and competitive dynamics. |
| Key Measures | Feedback on the effectiveness of MVPs, user surveys, and prototypes. | Market share, sales, income, and consumer satisfaction. |
Essentially, the Product Development Lifecycle concentrates on producing a product, whereas the Product Lifecycle is concerned with managing and improving the market performance of that product. Effective product management requires a fundamental understanding of these differences.
Why Understanding the Product Development Lifecycle is Crucial?
For your product to remain competitive over time, it is essential to understand the product development lifecycle. The following are significant reasons:
1. Enhanced Efficiency:
Use a structured development approach to maximize your resources and efforts. It assists you in avoiding typical mistakes and reduces resource waste, improving overall effectiveness.
2. Improved Quality:
You stand out for your capacity to change and enhance your product constantly. This is accomplished through the cyclical process built into the lifespan of product development. A higher-quality end product is the result.
3. Market Adaptability:
Adaption is essential to be competitive in a changing market. Understanding the product development lifecycle will enable you to respond quickly and effectively to shifting market trends and consumer feedback.
4. User-Focused:
Creating products that resonate with your target audience is essential for success. Your product will remain user-centric as it evolves if you understand the product development lifecycle well.
5. Cost-effectiveness:
A successful product development process effectively eliminates wasteful expenses. This renders your product affordable to maintain as well as to create.
6. Risk Mitigation:
By comprehending the product development lifecycle, you can identify possible problems before they become serious. This preemptive strategy lessens the likelihood of suffering expensive setbacks.
7. Promoting Innovation
The iterative structure of the product development lifecycle sparks innovation. It enables your team to try new things, adjust, and roll out innovative features or enhancements motivated by insightful customer feedback.
In conclusion, knowing the product development lifecycle is more than just academic; it’s a key tactic for guaranteeing your product’s long-term competitiveness. From idea inception through market validation, these seven steps lay out a logical course that results in goods that resonate with your target market. Accept the product development lifecycle, and you’ll see your interests thrive in the dynamic world of innovation, providing value and gratification to your customers.